コード設計を学びたい人におすすめの本はこちら

記事をご覧いただき、ありがとうございます。
今回の記事では、Vue.jsの状態管理ライブラリ Pinia について解説します。
そもそも、Vue.js について詳しく知らない方は、コチラの記事で紹介しているので、是非合わせてご覧ください!
状態管理ツール Pinia とは
Piniaとは、Vue.jsの状態管理ライブラリです。
Pinia を利用することで、複数のコンポーネント間で共有したデータを一元管理することが可能となり、より効率的にフロントエンド開発を進めることができます。
英語で学ぶ
Pinia is a state management library [ for Vue.js. ] (②)
( By leveraging Pinia, ) it (仮主語) becomes possible ( to centrally manage shared data [ across multiple components, ]) ( enabling more efficient development [ of frontend applications. ]) (②)
状態管理とは
状態管理は、Vue.jsアプリケーションにおいてコンポーネント間でデータを一貫して管理する手法です。
初めの段階では、Vue.jsではpropsやイベントを介してデータを受け渡しますが、アプリケーションの規模が拡大し、コンポーネントの階層やデータの受け渡しが増えてくると props や emits でのデータの管理が難しくなります。
英語で学ぶ
State management is a technique [ for consistently managing data ( between components in Vue.js applications. )] (②)
( In the initial stages, in Vue.js, ) data is passed ( between components through props and events. ) (-③)
However, ( as the application scales and < the complexity [ of component hierarchy and data propagation ]> increases, ) < managing data through props and emits > becomes challenging. (②)
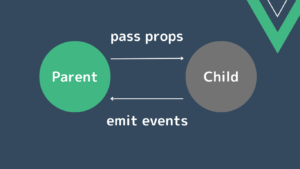

状態管理ライブラリを使用すると、アプリケーション全体で使用されるデータがストアと呼ばれる場所に配置されます。
このストアにより、データが一元管理され、異なるコンポーネントは同じデータにアクセスすることが可能になります。
英語で学ぶ
( When utilizing a state management library, ) < data [ used ( throughout the entire application )]> is placed ( in a location [ called a store. ]) (-③)
This store facilitates centralized management [ of data ], ( enabling different components < to access the same data. >) (③)
いつストアを使うのか
ストアは、アプリケーション全体で共有する必要のあるデータを保存する場所です。
例えば、ナビゲーションバーに表示されるユーザー情報など、アプリケーション内のさまざまな場所で利用されるデータは、ストアに適しています。
また、複雑な複数ステップのフォームなど、ページをまたいでデータを保持する必要がある場合もストアを使用します。
英語で学ぶ
A store is a storage location [ for data [ that needs < to be shared ( across the entire application. )>]] (②)
( For example, ) < data [ like user information [ displayed ( in the navigation bar, )]] [ which is utilized ( in various parts of the application, )]> is suitable [ for storage in a store. ] (②)
Additionally, stores are used ( when there is a necessity [ to retain data across pages, ]) ( such as in complex multi-step forms. ) (-③)
全てのコンポーネントがストアを使用する必要はありませんが、もしアプリケーションがグローバルな状態を必要とする場合、Piniaを使うことで開発がスムーズに進みます。
英語で学ぶ
Not all components need < to use a store, > but ( if an application requires global state, ) using Pinia can facilitate smooth development. (③)
リスニングする
Pinia の導入
Piniaのインストール
# npm を利用する場合
npm install pinia
# yarn を利用する場合
yarn add piniaプロジェクトの src ディレクトリ内にある main.js ファイルを開きます。そして、以下のように Pinia をインポートし、Vue インスタンスに追加します。
英語で学ぶ
Open < the main.js file [ located ( within the project’s src directory. )]> (③) Import Pinia and add it ( to the Vue instance as follows: ) (③)
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(createPinia())
app.mount('#app')上記のコードでは、createPiniaを使ってPiniaのインスタンスを作成し、app.use(createPinia())でVueアプリケーションに追加しています。
これで、PiniaがVueアプリケーションで使用できる状態になります。
英語で学ぶ
( In the above code, ) a Pinia instance is created ( using createPinia, ) and it is added ( to the Vue application with app.use(createPinia()). ) (-③) This configuration makes Pinia available [ for use within the Vue application. ] (⑤)
リスニングする
Pinia の使い方
defineStore
まずは、defineStore を利用して、Store(状態をデータとして保持する場所)を作成します。
第一引数には、Store を識別するための一意ないIDをつけ、第二引数に Options オブジェクトまたは、Setup 関数を受け取ることができます。
Optionsオブジェクトを渡してストアを定義する場合は、以下のプロパティを保持します。
- state プロパティ
- getters プロパティ
- actions プロパティ
それぞれのプロパティの役割については後ほど説明します。
Setup 関数を利用してストアを定義する方法もあります。
Composition API の setup 関数と同様に、リアクティブな値とメソッドを定義する関数を渡して、公開したいプロパティとメソッドを含むオブジェクトを返すことができます。
英語で学ぶ
( To begin with, ) create a Store ( using defineStore. ) (③)
Provide a unique ID ( as the first argument ) ( to uniquely identify the Store, ) and ( as the second argument, ) you can either pass an Options object or a Setup function. (③)
( When defining a store by passing an Options object, ) include the following properties: (③)
- state property
- getters property
- actions property
< The roles [ of each property ]> will be explained later. (-③)
< Another way [ to define a store ]> is < to use the Setup function. > (②)
( Similar to the Composition API’s setup function, ) pass < a function [ that defines reactive values and methods. ]> Return < an object [ containing the properties and methods [ you want to expose. ]]> (③)
リスニングする


Options Stores を使ったサンプルコードはコチラ
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
},
actions: {
increment() {
this.count++;
},
decrement() {
this.count--;
},
reset() {
this.count = 0;
},
},
});Setup Stores を使ったサンプルコードはコチラ
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(0);
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2);
const increment = () => {
count.value++;
};
const decrement = () => {
count.value--;
};
const reset = () => {
count.value = 0;
};
return {
count,
doubleCount,
increment,
decrement,
reset,
};
});Setup Stores を使った場合:
ref()がstateプロパティに相当computed()がgettersプロパティに相当function()がactionsプロパティに相当
Options Stores と Setup Stores のどちらかを使うかは、公式サイトのよると以下のような説明となっています。
As with Vue’s Composition API and Options API, pick the one that you feel the most comfortable with. If you’re not sure, try Option Stores first.
—————————————-
Vue の Comboposition API と Options API と同様に、最も使いやすいものを選択してください。よくわからない場合は、まずオプション ストアを試してください。
今回の記事では、Options Stores の扱い方について紹介します。
英語で学ぶ
If using Setup Stores:
- ref() corresponds ( to the state property. )
- computed() corresponds ( to the getters property. )
- function() corresponds ( to the actions property. )
The official website explains < whether to use Options Stores or Setup Stores as follows. > (③)
( In this article, ) we will introduce < how to handle Options Stores. > (-③)
state
stateは、アプリケーション全体で共有されるデータを定義する場所で、state で定義された値は、異なるコンポーネント間でアクセス可能で、値が共有されます。
英語で学ぶ
State is ( the place ※ 省略) [ where you define < data [ that is shared ( across the application, )]>] (②) and < values [ defined ( in state )]> are accessible (②) and shared ( between different components. ) (-③)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
export const useTodoStore = defineStore('todo', {
state: () => ({
tasks: [],
}),
});<script setup>
import { useTodoStore } from './store/todo';
const todoStore = useTodoStore();
console.log(todoStore.tasks); // タスクの取得
</script>このように、useTodoStore()でtodoストアのインスタンスを取得し、そのインスタンスを使ってstateの中のtasksにアクセスできます。
これにより、アプリケーション内の異なる部分で同じデータにアクセスできるようになります。
英語で学ぶ
( In this way, ) you can use useTodoStore() ( to obtain a todo store instance ) and use that instance ( to access tasks [ in state. ]) (③)
This allows you < to access the same data [ in different parts of your application. ]> (⑤)
getters
gettersは、アプリケーションの状態(state)から派生したデータを計算したり、加工したりするために利用されます。gettersを使用することで、コンポーネントなどからこれらの計算されたデータにアクセスできます。
英語で学ぶ
Getters are used ( to compute and manipulate data [ derived from application state. ]) (-③) ( By using getters, ) you can access < these calculated data [ from components etc. ]> (③)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
export const useTodoStore = defineStore('todo', {
state: () => ({
tasks: [],
}),
getters: {
completedTasks: (state) => state.tasks.filter(task => task.completed),
},
});上記の例では、completedTasksはtasks内の完了したタスクだけを取得するgettersです。
英語で学ぶ
( In the above example, ) completedTasks is < a getter [ that retrieves only completed tasks [ from tasks. ]]> (②)
<script setup>
import { useTodoStore } from '@/stores/todo';
const todoStore = useTodoStore();
console.log(todoStore.completedTasks); // 完了したタスクの取得
</script>上記のように、gettersを利用することで、state を算出したプロパティにアクセスすることができます。
英語で学ぶ
( As in the above code, ) < using getters > enables access [ to properties derived from the state. ] (③)
actions
actionsは、ストア内で必要なビジネスロジックを定義します。
actionsを使用することで、コンポーネントからこれらのメソッドを呼び出すことができ、state の値を更新することができます。
英語で学ぶ
actions define < the business logic [ required within your store. ]> (③)
Actions allows your component < to call these methods > and < update the value [ of state. ]> (⑤)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
export const useTodoStore = defineStore('todo', {
state: () => ({
tasks: [],
}),
actions: {
addTask(newTask) {
this.tasks.push(newTask);
},
},
});
<script setup>
import { useTodoStore } from '@/stores/todo';
const todoStore = useTodoStore();
todoStore.addTask({ text: 'New Task', completed: false }); // タスクの追加
</script>上記のコードのように、コンポーネントから actions を呼び出すことで、state のデータが更新されます。
英語で学ぶ
( As in the above code, ) < calling actions [ from a component ]> allows ( for the updating of data in the state. ) (①)
storeToRefs
storeToRefsは、Piniaのユーティリティ関数で、リアクティブを担保しながら、Storeからプロパティを参照するために使用されます。
storeToRefsを利用せず、Sotreのプロパティを分割代入すると、リアクティブな性質を失ってしまうため、storeToRefs関数を利用する必要があります。
英語で学ぶ
storeToRefs is < a utility function in Pinia [ that is used ( to reference properties from a Store )] ( while ensuring reactivity. )> (②)
( If you use destructuring ( to directly assign properties from a Store ) ( without using storeToRefs, )) you lose the reactive nature. Therefore, (③) it (仮主語) is necessary ( to use the storeToRefs function. ) (②)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({
counter: 0,
counterToRefs: 0,
}),
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.counter * 2,
doubleCountToRefs: (state) => state.counterToRefs * 2,
},
actions: {
increment() {
this.counter++;
this.counterToRefs++;
},
},
});
<template>
<div>
<div>Counter: {{ counter }}</div>
<div>DoubleCount: {{ doubleCount }}</div>
<hr />
<div>CounterToRefs: {{ counterToRefs }}</div>
<div>DoubleCountToRefs: {{ doubleCountToRefs }}</div>
<button @click="counterStore.increment()">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from './store/counter';
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia';
const counterStore = useCounterStore();
const { increment } = counterStore;
const { counter, doubleCount} = counterStore;
const { counterToRefs, doubleCountToRefs } = storeToRefs(counterStore);
</script>上記のサンプルコードで、+ボタンを5回クリックした後の、ストアのデータの値と画面結果はコチラ
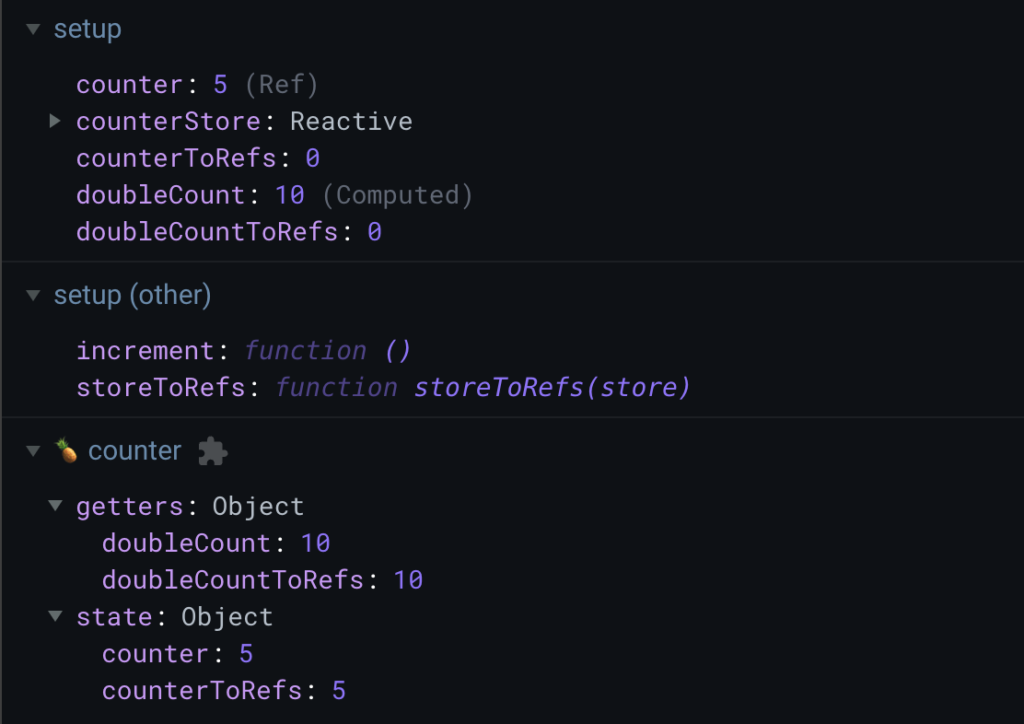

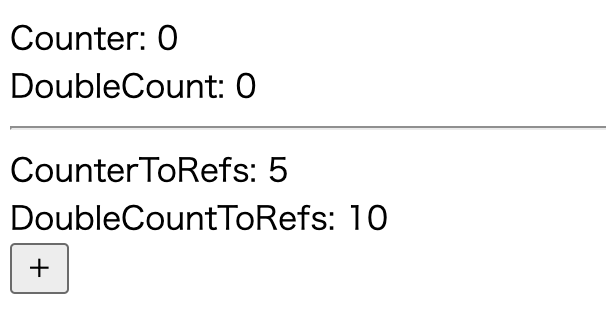

ストアで管理しているデータは、正常にインクリメントされているにもかかわらず、画面に表示している counter DoubleCounter は0のままです。
これは、storeToRefs を利用していないため、リアクティブな性質を失ったのが原因です。
英語で学ぶ
( Although the data managed by the store is incremented normally, ) < the counter Double and Counter > displayed ( on the screen remains 0. ) (①)
This is ( because it no longer uses storeToRefs, so it loses its reactive nature. ) (①)






